一、背景:MCP 协议介绍
在 AI 蓬勃发展的当下,大型语言模型(LLM)虽展现出强大潜力,却受困于与外部资源连接的难题。数据分散、接口繁杂,致使 AI 模型难以灵活对接本地资源与远程服务,极大限制了其响应质量与工作效率。而就在这一关键时刻,MCP Server 强势登场,成为破局的关键力量。尤其随着 Manus 的火爆出圈,MCP Server 也备受瞩目,迎来了飞速发展,短短 1 个多月时间,数量已超 5000 个 。
MCP Server,即模型上下文协议服务器,基于 Anthropic 公司 2024 年 11 月开源的模型上下文协议(MCP)构建,是一款轻量级服务程序。MCP 协议采用客户端 - 服务器(Client-Server)架构。客户端(MCP Client)负责与服务器建立稳固连接,并按需发起各类请求;服务器端则精准解析请求,调用对应资源或工具处理任务,再将处理结果及时反馈给客户端。MCP 协议的诞生,旨在攻克 AI 应用中的数据与接口难题,为开发者提供标准化接口,让 AI 模型能够自由穿梭于本地与远程资源之间,显著提升 AI 助手的表现。下图是 MCP 协议的基本交互关系示意图:
sequenceDiagram
participant Client as Claude Desktop<br/>(MCP Client)
participant Server as MCP Server
participant LLM as 大型语言模型
Client->>Server: 1. 请求可用函数列表
Client->>LLM: 2. 发送用户提问+可用函数列表
LLM-->>Client: 3. 返回所需函数名称和对应参数
Client->>Server: 4. 调用函数(functionName, parameters)
Server-->>Client: 5. 返回函数执行结果
Client->>LLM: 8. 转发执行结果
LLM-->>Client: 9. 返回最终回答或下一步所需函数调用
Note over Client,LLM: MCP协议实现了大模型与外部工具的标准化连接
二、OpenAPI2MCPtools 开源项目
仔细翻阅当前公开的 MCP Server 清单可以发现,目前主要的 MCP Server 集中在桌面端软件,更多是方便个人用户和开发者。对企业内部广泛存在的现有软件系统,并没有高效兼容的方案。比如 OpenAPI2MCPtools 开源项目,看似只需要下面这样三十行代码,就可以将现存软件的 OpenAPI 规范,快速封装成 MCP Server 的 tools,供 AI 调用。
import { Server } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/index.js';
import { StdioServerTransport } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js';
import { CallToolRequestSchema, ListToolsRequestSchema, } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/types.js';
import { Converter } from 'openapi2mcptools';
import * as fs from 'fs';
import * as yaml from 'js-yaml';
const converter = new Converter({ });
const yamlContent = fs.readFileSync('Api_5.3_schema.yaml', 'utf8');
const my_specs = yaml.load(yamlContent);
await converter.load(my_specs);
const tools = converter.getToolsList();
const toolCaller = converter.getToolsCaller();
const server = new Server({
name: 'my_server',
version: '1.0.0',
}, {
capabilities: {
tools: {},
},
});
server.setRequestHandler(ListToolsRequestSchema, async () => {
return {
tools,
};
});
server.setRequestHandler(CallToolRequestSchema, async (request) => {
return await toolCaller(request);
});
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);
然而,在实际的大规模系统环境下,这个项目存在一个核心问题:**当 API 数量较大时,MCP Server 的 tools 数量急剧膨胀,远超大模型能有效处理的上下文窗口极限,会导致 AI 对话完全不可用。如下图所示:
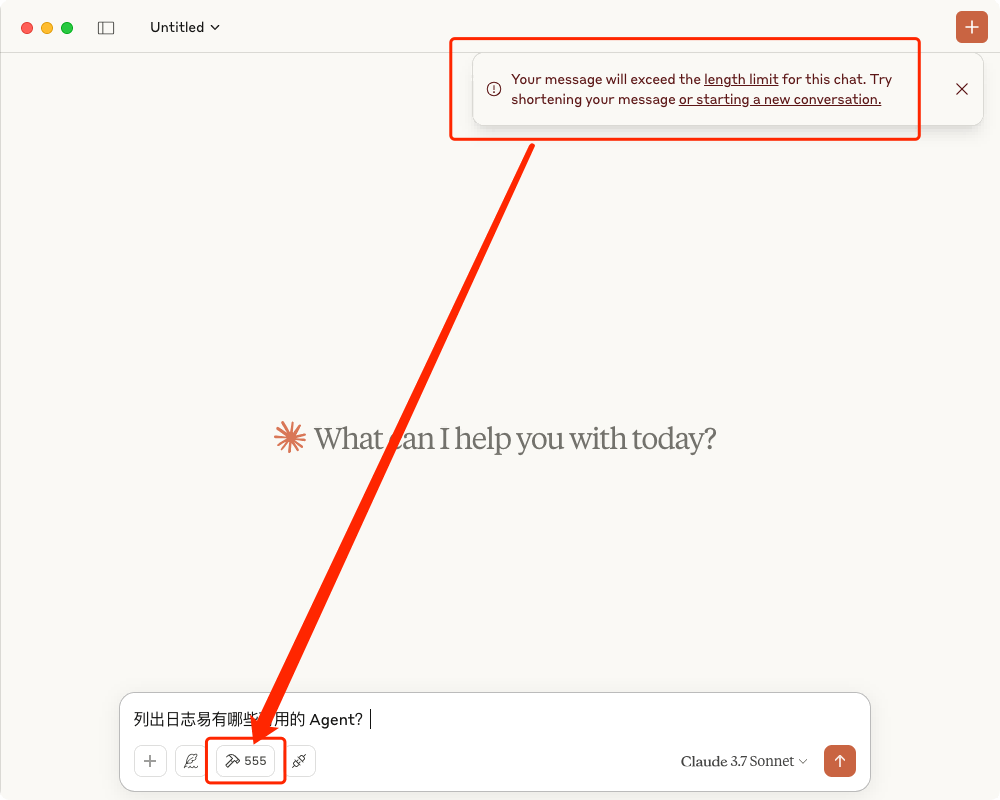
三、日志易MCP Server实现路径
为了解决这个问题,日志易MCP Server采用了模块化设计思路,利用 OpenAPI 规范中的 Tag 对象作为语义抽象层,构造了 MCP Server 的模块初筛和功能复筛工具,实现了对 OpenAPI 规范的动态加载与按需调用。最终,使得 AI 对话能够流畅进行,任意调用日志易 API 功能,而不会因为上下文窗口的限制而中断。
sequenceDiagram
participant User as 用户
participant LLM as 大型语言模型
participant MCP as MCP服务器
participant ModuleSelector as 模块初筛层
participant APISelector as 功能复筛层
participant APIExecutor as API工具调用层
participant Cache as 模块缓存管理
participant Parser as OpenAPI解析器
participant HTTPClient as HTTP客户端
participant API as 企业API系统
User->>LLM: 发送查询请求
LLM->>MCP: CallTool(select_modules)
MCP->>ModuleSelector: 获取模块列表
alt 首次加载
ModuleSelector->>Parser: 解析OpenAPI规范
Parser->>ModuleSelector: 返回模块化API定义
ModuleSelector->>Cache: 存储模块信息
else 已缓存
ModuleSelector->>Cache: 获取模块信息
Cache->>ModuleSelector: 返回缓存的模块信息
end
ModuleSelector->>MCP: 返回模块列表
MCP->>LLM: 提供可用模块列表
LLM->>MCP: CallTool(select_apis_from_module, 模块名)
MCP->>APISelector: 获取指定模块的API列表
APISelector->>Cache: 获取模块的API详情
Cache->>APISelector: 返回API详情
APISelector->>MCP: 返回API列表和规范
MCP->>LLM: 提供可用API详情
LLM->>MCP: CallTool(gencode_callapi, path, method, parameters)
MCP->>APIExecutor: 执行API调用
APIExecutor->>HTTPClient: 构建HTTP请求
HTTPClient->>API: 发送API请求
API->>HTTPClient: 返回API响应
HTTPClient->>APIExecutor: 处理响应结果
APIExecutor->>MCP: 返回API执行结果
MCP->>LLM: 提供API响应数据
LLM->>User: 生成最终回答
最终效果如图:

四、日志易 MCP Server典型应用场景和演进方向
- 涉及用户及权限管理类的 API 操作
- 数据处理流程中,综合调用 Agent 采集、字段提取类 API 进行一站式处理
- 辅助用户在 AI 分析过程中,快速创建对应的监控告警规则,或工单响应评论



